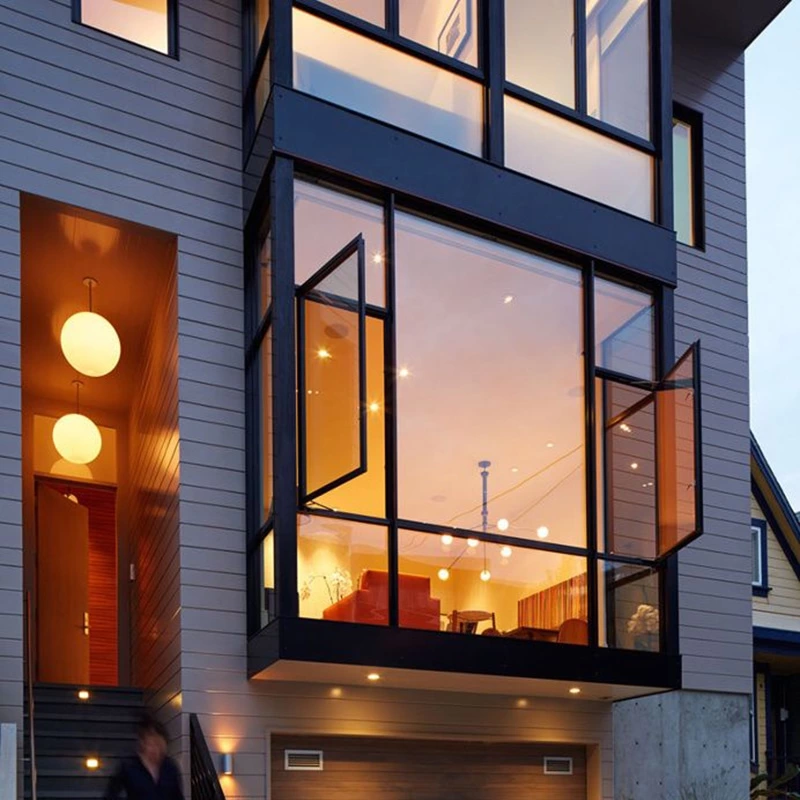
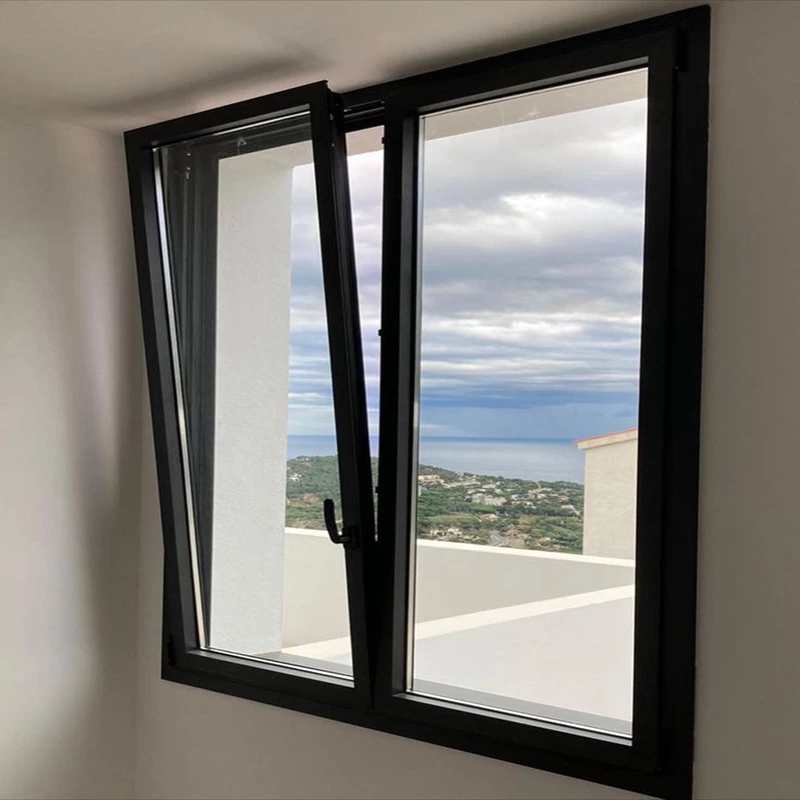
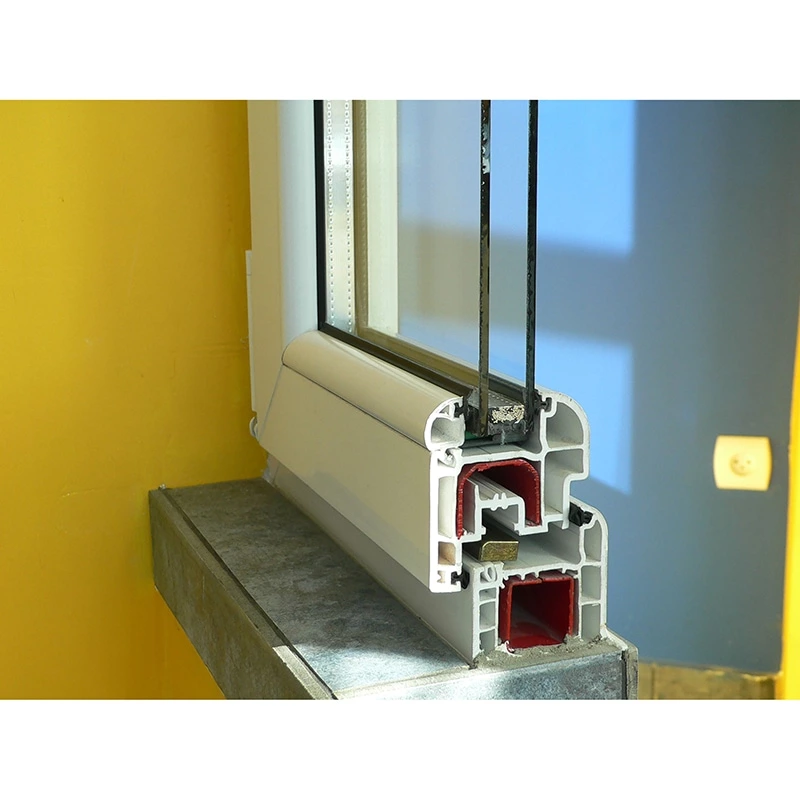
Window
Doors and windows serve several essential purposes in architecture:
- Access and Security Control: Doors and windows provide primary access points for entering and exiting buildings, while also controlling security by restricting unauthorized entry.
- Daylighting and Ventilation: Windows allow natural light to enter indoor spaces, reducing the need for artificial lighting and facilitating air circulation to maintain fresh and comfortable indoor environments.
- Visual Connection and Aesthetics: Doors and windows enable occupants to enjoy views of the external environment, enhancing the architectural appearance and decorative aspects of buildings.
- Sound Insulation and Thermal Control: Properly designed doors and windows effectively insulate against noise and heat, improving indoor comfort levels.
- Style and Functionality: The design and selection of doors and windows can be optimized to complement architectural styles, functional requirements, and climatic conditions, achieving a balance between aesthetic appeal and practicality.
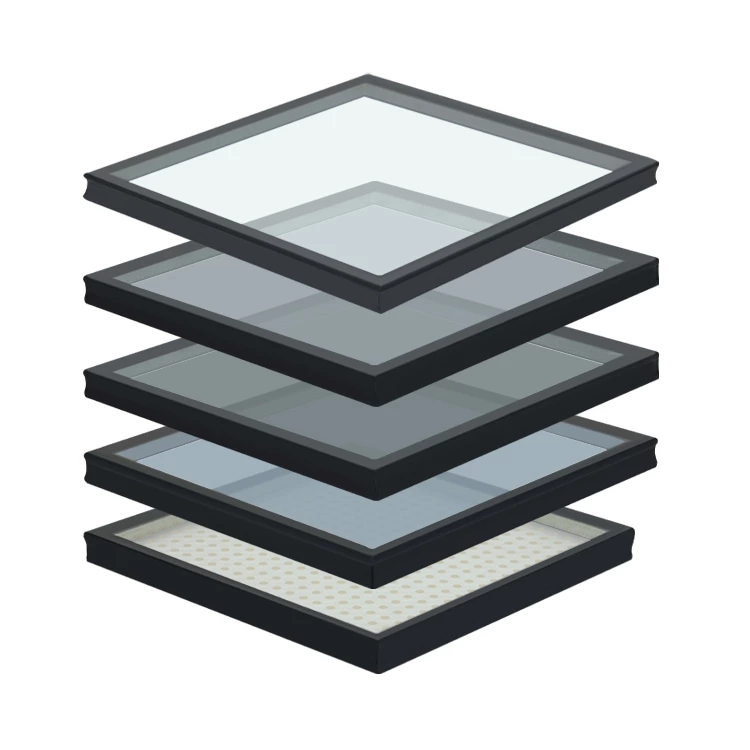
Different Glass Chosen:

Tempered Glass:
Tempered glass is produced through special heating and rapid cooling processes. This process creates compressive stresses on the surface and tensile stresses inside, significantly increasing its strength. When broken, tempered glass shatters into small granular pieces, reducing the risk of sharp edges and potential injuries. This characteristic makes tempered glass widely used in applications requiring high security, such as doors, windows, stair railings, and curtain walls.
Laminated Glass:
Laminated glass consists of two glass panes bonded together with a layer of special plastic film in between. This plastic film, typically made of polyethylene or polypropylene, effectively prevents the glass from shattering into sharp pieces upon impact, enhancing window safety. Even if the glass breaks, the film holds the fragments together, minimizing potential harm. Therefore, laminated glass is extensively used in places requiring heightened security and anti-theft capabilities, such as financial institutions and commercial centers.
LOW-E Glass:
Low-E glass is coated with a special metal oxide layer on the glass surface or between glass layers. This coating effectively reflects indoor heat, reducing heat loss in winter and preventing solar heat gain in summer. Compared to traditional glass, low-E glass helps lower heating costs during colder months and reduces the load on air conditioning systems during hotter months, thereby conserving energy
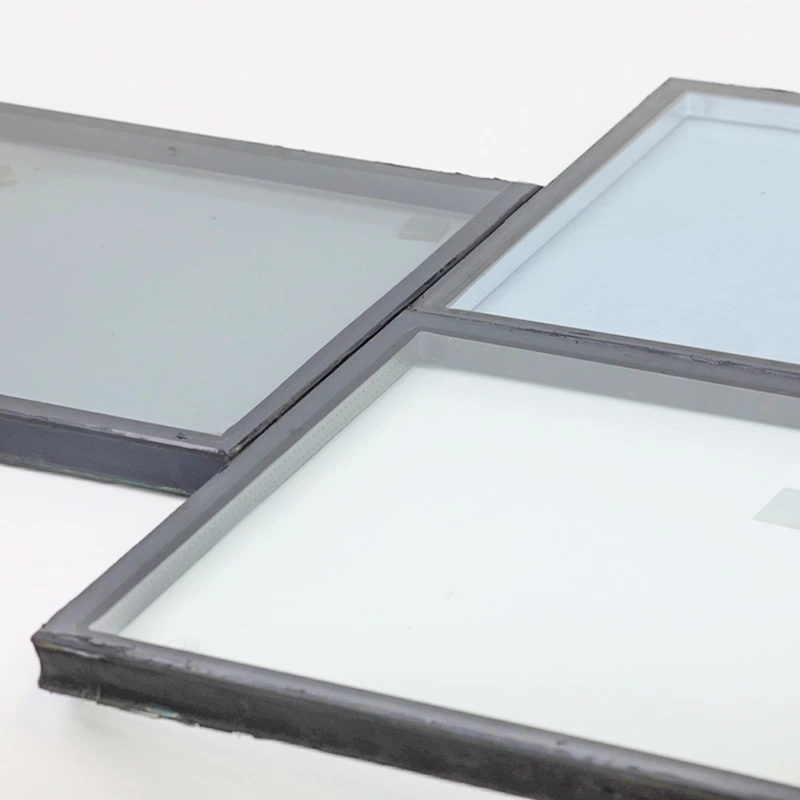
Insulated Glass:
Insulating Glass Units (IGUs) are constructed by sealing two or more glass panes with air or inert gas in between. They offer superior thermal and acoustic insulation, reducing energy consumption and indoor noise levels while enhancing building safety and comfort. That is most commonly used for window.